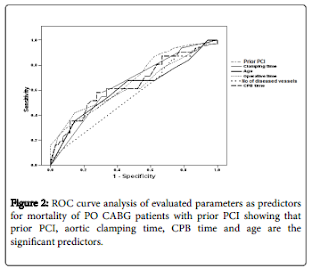
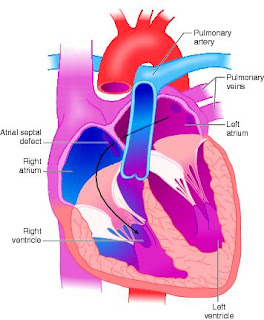
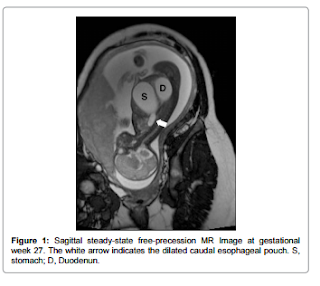
Atrial
fibrillation (AF) is the most frequent heart rhythm disorder in clinical
practice. Many conditions could predispose the development of AF such as
hypertension, heart failure, valvular heart disease, aging, coronary artery
disease, diabetes mellitus, and sleep apnoea.
Kocyigit and
colleagues reported a study to investigate the association between epicardial
adipose tissue (EAT) thickness and AF recurrence after cryoballoon-based pulmonary
vein isolation (PVI). A total of 249 patients (55.6 ± 10.7 years; 48.2% male;
18.5% persistent AF were followed-up for 29 months (8 months-48 months). AF
after the ablation procedure was 75.9% at a median follow-up of 29 months.
Total
periatrial EAT thickness (18.1 ± 6.2 vs. 14.7 ± 4.7 mm; P<0.001) was greater
in patients with late AF recurrence when compared to those without.
Periventricular or total EAT thickness measurements did not differ between both
groups (P>0.05). Multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression analysis
showed that periatrial EAT thickness (hazard ratio, 1.086; P=0.001) and left
atrial volume index (hazard ratio, 1.144; P<0.001) were independent
predictors for late AF recurrence. EAT thickness may serve as a beneficial parameter
for prediction of AF recurrence after cryoballoonbased PVI.Read more.....